What is Nonenal? The Cause of 'Old People Smell™'
Nonenal® (also known as 2-Nonenal) is a naturally occurring compound responsible for the distinct odor associated with aging. It typically appears after age 40, becoming more noticeable in both men and women.
As we age, changes in body chemistry cause skin lipids to oxidize, producing Nonenal. This odor is persistent, greasy, and often compared to old books or stale oil and it doesn’t wash away easily with regular soap or body wash.
Understanding and managing Nonenal is key to maintaining a fresher personal scent and supporting confidence and well-being as we age.
Why Do Old People Smell Differently?
The term "old people smell" isn’t about poor hygiene it’s a natural and scientifically proven part of the aging process. As we grow older, especially after the age of 40, our bodies begin to produce more omega-7 unsaturated fatty acids. These fatty acids oxidize on the skin and lead to the formation of nonenal, a compound responsible for the distinct aging body odor.
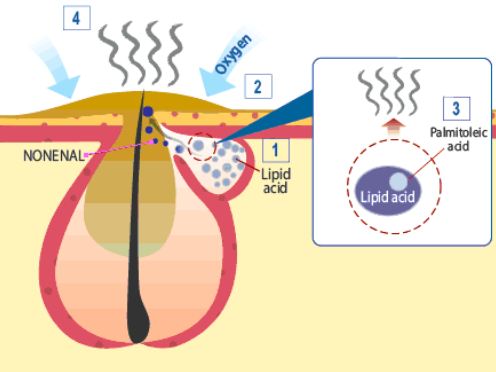
The emergence of nonenal is scientifically linked to the degradation of skin lipids. As we age, the skin's ability to regenerate declines, leading to the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. The result is the formation of nonenal, a compound with a distinctly unpleasant smell.
Nonenal is produced when omega-7 unsaturated fatty acids on the skin react with oxygen, a process called lipid peroxidation.
How Mirai Clinical Eliminates Old People Smell?
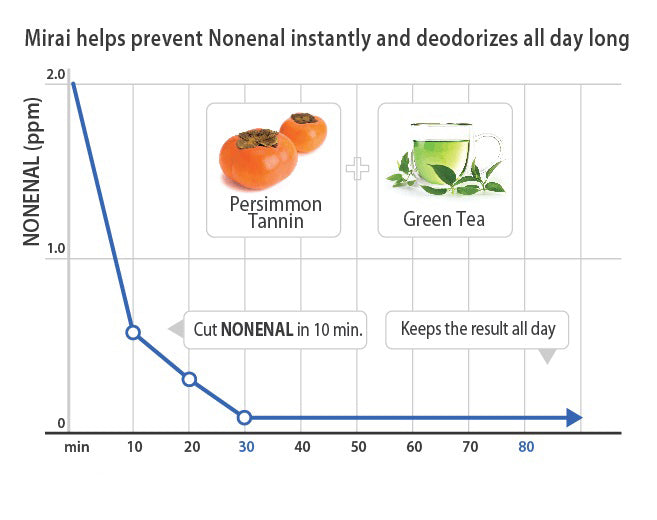
At Mirai Clinical, we have developed a natural and effective solution to tackle nonenal our line of products formulated with Japanese persimmon extract.
Persimmon extract has been scientifically proven to break down nonenal molecules, effectively eliminating old people's smell without using harsh chemicals or synthetic fragrances. Try Our Deodorizing Soap with Persimmon mainly effective in neutralizing nonenal aging odor.
- Dermatologist-tested and made in Japan
REFERENCES:
1. Lipid Peroxidation Generates Body Odor,Journal of Biological Chemistry
2. Download PDF:“Odor Associated with Aging” from Anti-Aging Medicine
3. Do Older People Actually Smell Different? Healthline
4. The Smell of Age: Perception and Discrimination of Body Odors of Different Ages